Conflict cannot survive without your participation. - Wayne Dyer
When do merge conflicts occur?
A conflict arises when git is unable to automatically merge changes between two commits.
This happens when the same line of code is changed on multiple sources. Conflict often happens when multiple people work on the same branch, but it can also happen when working on the same lines of code in different branches.
Example:
Developer A and Developer B checkout code from the same remote repository and work on the same file. Developer A then pushes their code to the remote repository. Afterwards, developer B tries to push their changes to the same remote repository. However, he is unable to push the code and is greeted with the Merge conflict message instead.
How to recognize conflicted files?
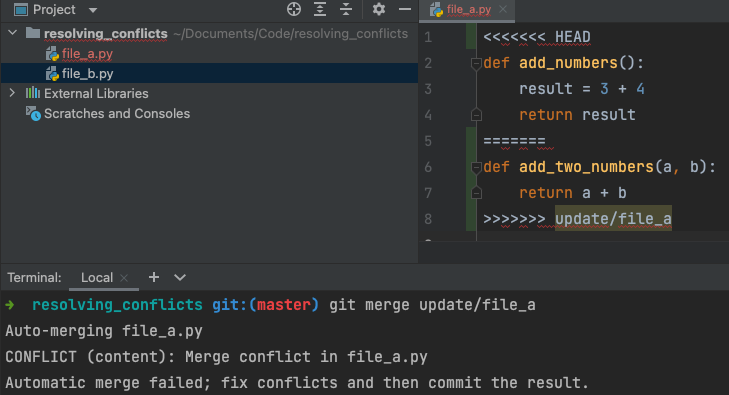
When a conflict occurs, you will immediately notice a conflict message in the terminal.
The conflicted file will also be marked red in the project view. When you open the file, you will notice additional lines in the file.
<<<<<<< HEAD
Content from e.g. main branch
=======
Content from some new branch
>>>>>>> branch_being_merged
The ======= marks the center of the conflict, i.e. divides the content between the two conflicting sources. Everything between <<<<<<< HEAD and ======= is the content from the current branch to which the HEAD reference points. Everything between ======= and >>>>>>> branch_being_merged is the content in the branch you are trying to merge.
How to resolve conflicts?
There are a few ways to resolve conflicts. The easiest one is to open the conflicted file through a text editor or an IDE and make the necessary changes.
When resolving conflicted files, there are multiple approaches. Depending on how complicated the conflict is, you might prefer to use one over the other.
Approach 1
The most straightforward approach.
- Open the conflicted file and make the necessary changes
Nice and easy if there is a minor conflict. In case of multiple conflicted files or lines in a large file, it might get confusing.
Approach 2
If you only want to keep the changes from one branch and don't care about the changes from the other one. You can simply accept all the changes from either branch.
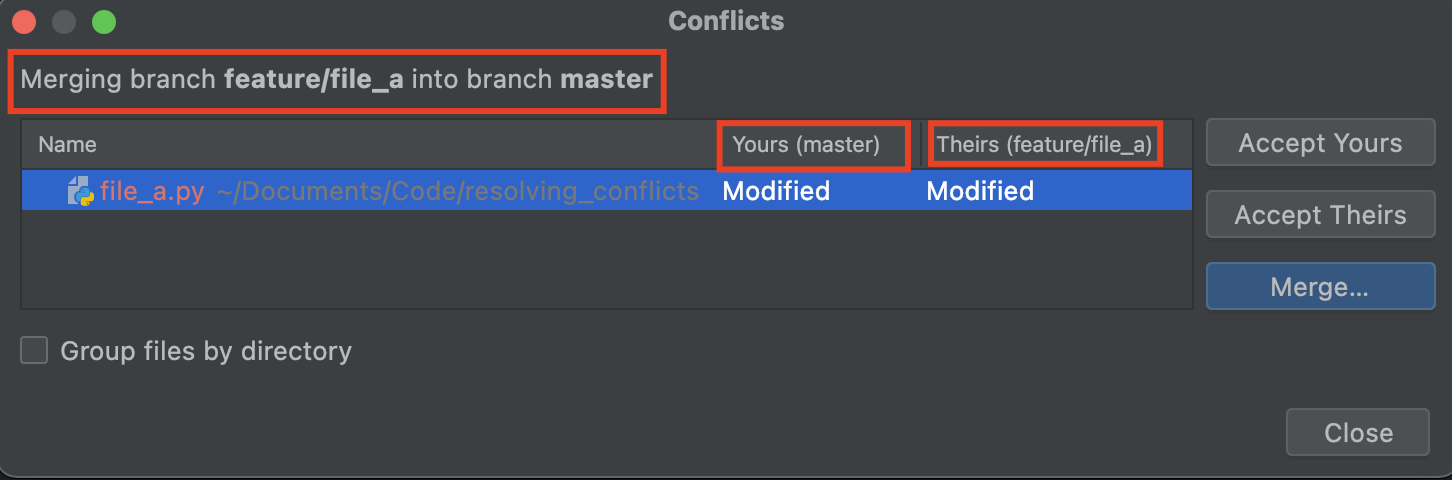
- Open the project view
- Right-click the conflicted file
- Select Git -> Resolve Conflicts...
- Conflicts window opens
- Note the title and column names in the window, clearly stating what is being merged
- Select Accept Theirs to accept the changes from the merging branch
- Alternatively, select Accept Yours to accept the changes from the current branch (the branch you are merging into)
Approach 3
Use this approach if there are quite a few changes throughout the entire file, and you want to cherry-pick changes from both branches.
- Open the project view
- Right-click the conflicted file
- Select Git -> Resolve Conflicts...
- Conflicts window opens
- Double-click the conflicted file
- A window showing the content in the file from both branches opens
- On the left-hand side is the file from the branch you are merging into
- On the right-hand side is the file from the merging branch
- Click the double-arrow (
>>or<<) next to the lines of code (from the left-hand or the right-hand side) that you want to keep- This will add the code to the Result (content in the middle view) which is the content you wish to keep
- Alternatively, click the
Xbutton next to the lines you do not want to keep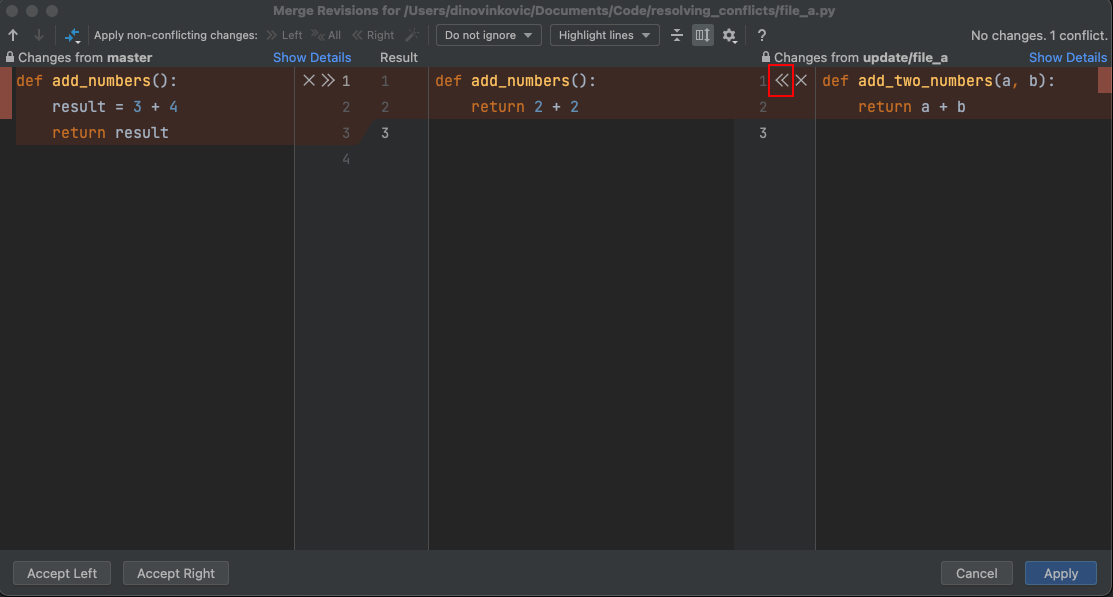
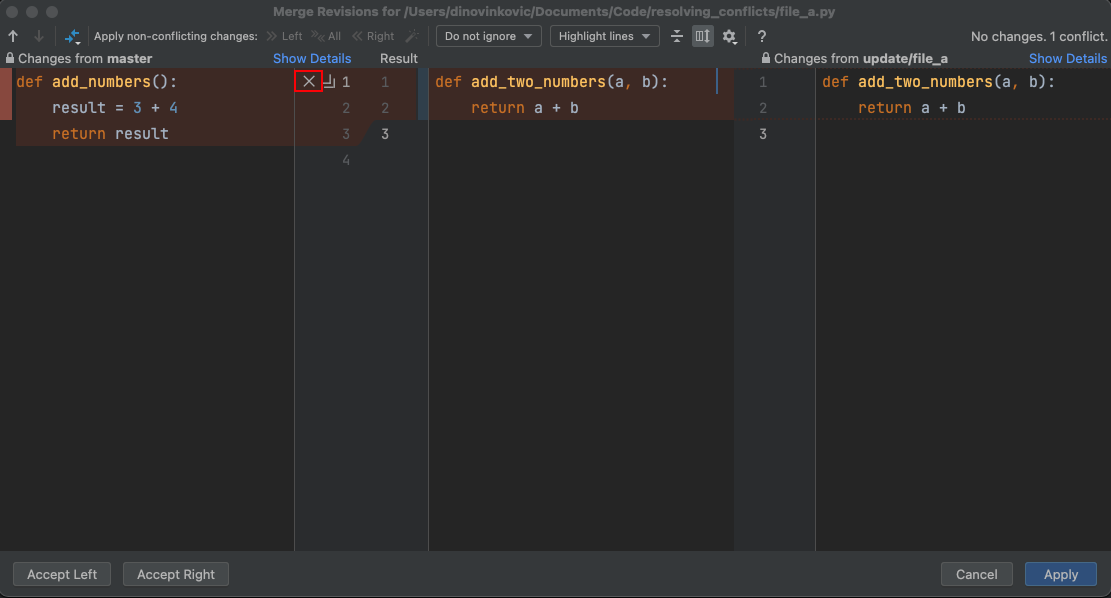
- Click Apply when you resolved all conflicts
- Noted by All conflicts resolved message in the upper-right corner
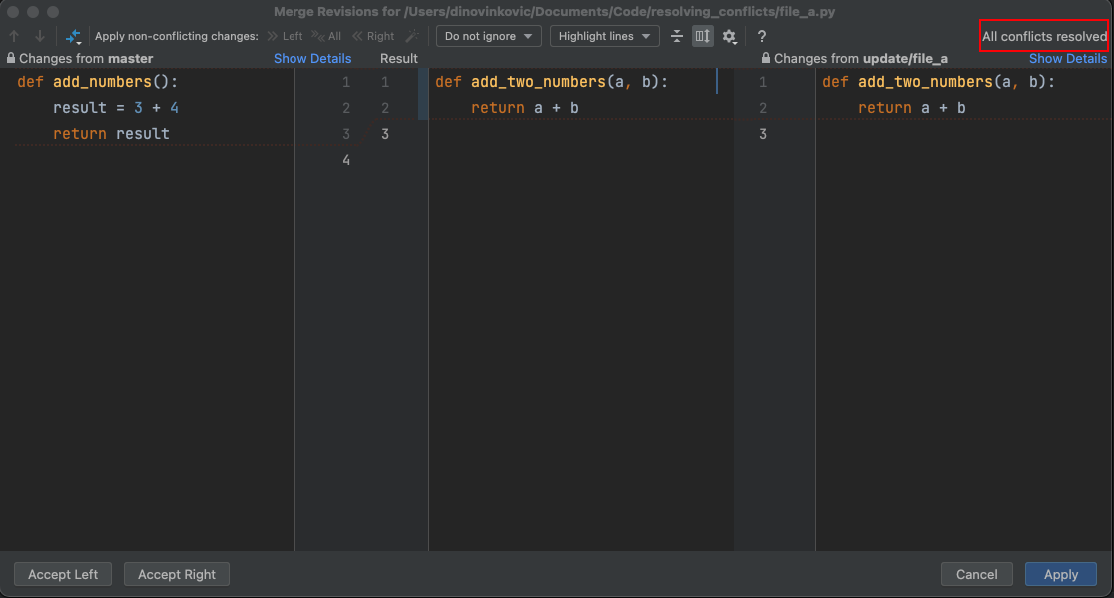
- Noted by All conflicts resolved message in the upper-right corner
Saving changes
Once you resolved all the conflicts, you are still not done. First make sure everything is in order, then commit and push the changes.
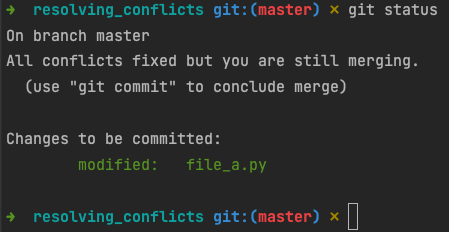
- Open the terminal
- Run
git status- You should see a message saying all conflicts are fixed
- Commit and push the changes
Resolving conflicts in a version control system
When using a VCS like GitHub or Bitbucket, you will see a warning after opening a pull request in case of a conflict. If that happens, fix the code on your machine and push the changes. Once you are done, if everything is ok, the warning should be gone.
- Open the branch you were working on in PyCharm
- Make the necessary changes to resolve the conflicts
- Commit and push the changes
- Verify that the conflict warning is no longer shown in the VCS