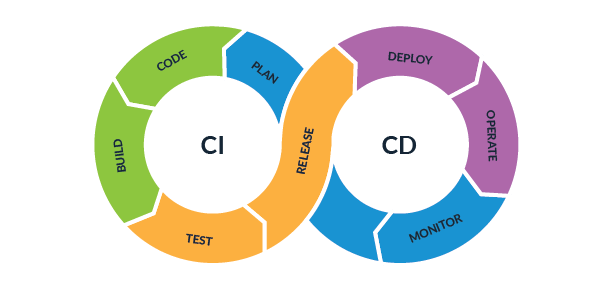
CI/CD, short for Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery/Continuous Deployment, is all about making software development and deployment easier by automating tasks. It helps teams deliver high-quality code changes to production quickly and reliably.
Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration means frequently adding code changes to a shared place like Git, where automated tests are run. The goal is to catch any issues early on and keep the code stable. With CI, developers regularly add their changes, and each time they do, the system checks the code automatically. If there are any problems, developers get notified right away, so they can fix them quickly. This way, mistakes are smaller and easier to handle.
Continuous Delivery
Continuous Delivery is about automatically sending code changes to production or a test area in a consistent way. When code changes pass the automated tests from CI, they're sent to a testing area. There, more tests can happen or people can check it before it goes to production. This helps make sure changes are always ready to be sent out to users quickly and confidently.
Continuous Deployment
Continuous Deployment is like a step further from Continuous Delivery. It means every time code changes pass the tests from CI, they're automatically sent to production without people having to do anything. This speeds up the process even more, getting changes to users faster and helping teams get feedback quickly.
Conclusion
In summary, CI/CD is a set of practices that enable teams to automate the process of building, testing, and deploying software changes quickly and reliably. In a way, it is an agile practice translated to writing code and deployment processes.