You can see a lot by just looking.
How to change remote repository URL
Let’s say you want to clone someone's GitHub repository but wish to continue pushing the changes to a new (your) remote repository.
Use the git remote set-url command to change your remote’s URL.
Clone a repository to your machine
git clone https://github.com/username/repository.gitCreate a new GitHub repository
Open the terminal and change the current working directory to your local project
cd repositoryChange your remote's URL
If updating to HTTPS:
git remote set-url origin https://github.com/USERNAME/REPOSITORY.gitIf updating to SSH:
git remote set-url origin git@github.com:USERNAME/REPOSITORY.git
Verify that the remote URL has changed
git remote -vStage, commit and push :)
Working with branches
Every project starts with the main branch, i.e. a main line of development. Sometimes you may want to try something out, have another version of your work or start working on a new feature and have it separate from the main. This is where branching comes in handy.
By creating a branch you are creating an independent line of development in which you can continue your work without having to fear messing something up in the main branch. Branching is a common practice among developers when introducing a new feature or updating the existing ones.
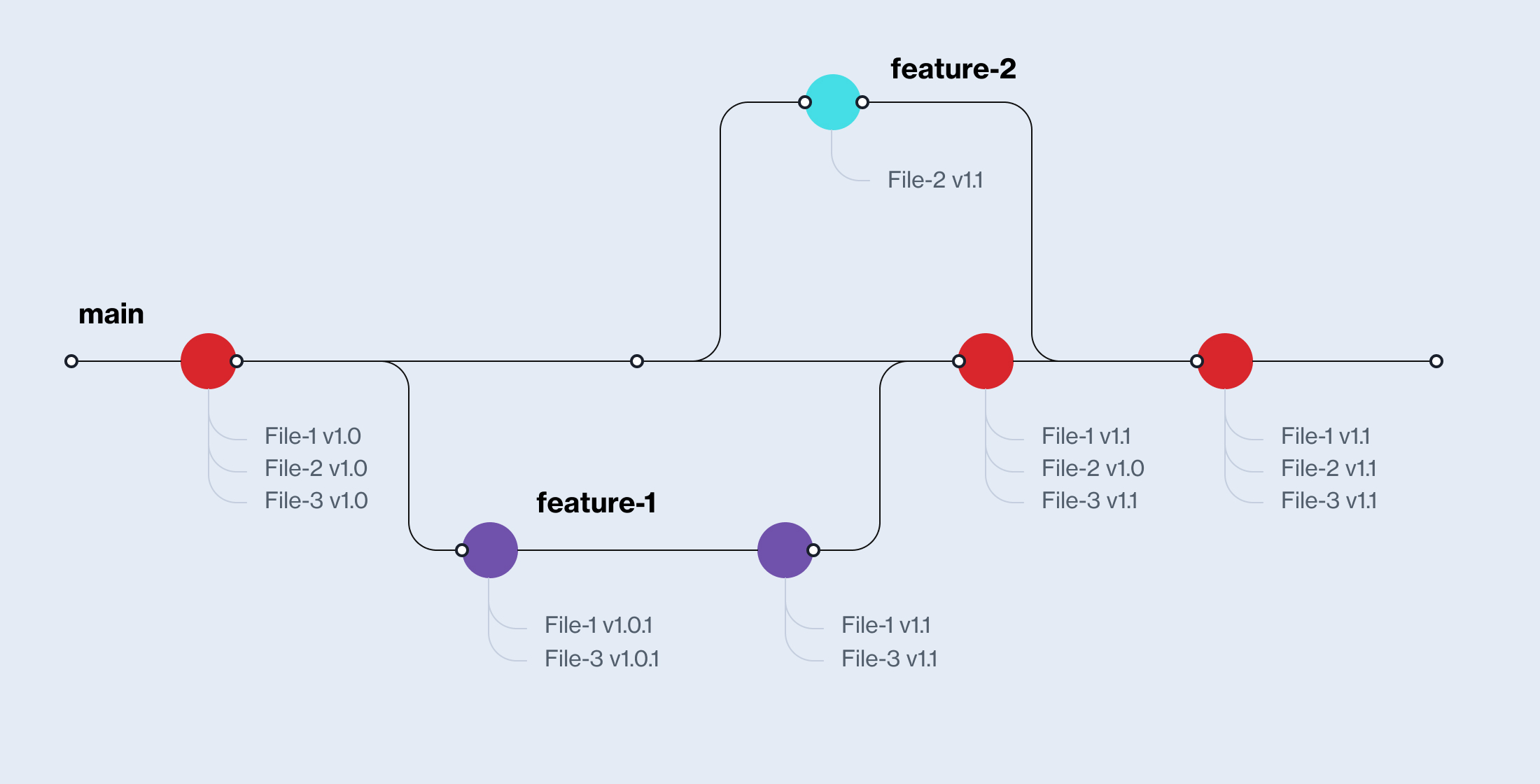
How to switch branches
Let’s say a project already exists, and you want to pull the updates and continue working on one of the branches.
Open the terminal and position to your project
cd repositoryPull the updates from the remote repository
git pullChange into the existing branch called
feature-1git checkout feature-1Make the changes to files
Stage, commit and push :)
How to create a new branch
There are multiple ways to create a new branch. This example shows how to create a new branch from the branch you are currently at.
Open the terminal and position to your project
cd repositoryCreate a new branch called ‘feature-abc’ from the branch you are currently at
git branch feature-abcView the branches on your local machine
git branchSwitch to the newly created branch
git checkout feature-abcEdit, stage and commit your files
Push the new local branch to the remote repository
git push
How to merge branches
To merge branches means to join their development histories together, i.e. to integrate the branch you worked on back into the branch from which it was created.
For example, you created a new branch from the main branch and after you committed the changes and made sure everything works, you want to merge it into the main.
Note that git merge merges the specified branch into the currently active one. If you want to merge into the main branch, you have to be on the main branch.
Open the terminal and position to your project
cd repositoryView the branches and make sure that you are on the main branch
git branchMerge the branch into the main branch
git merge feature-abc
How to create a pull request (GitHub)
A pull request is a way of notifying the collaborators on the project about the changes. Those changes can then be reviewed before being integrated into the main branch.
Go to GitHub and open the repository’s main page
From the branch dropdown menu in the upper left corner, select the branch that contains your commits
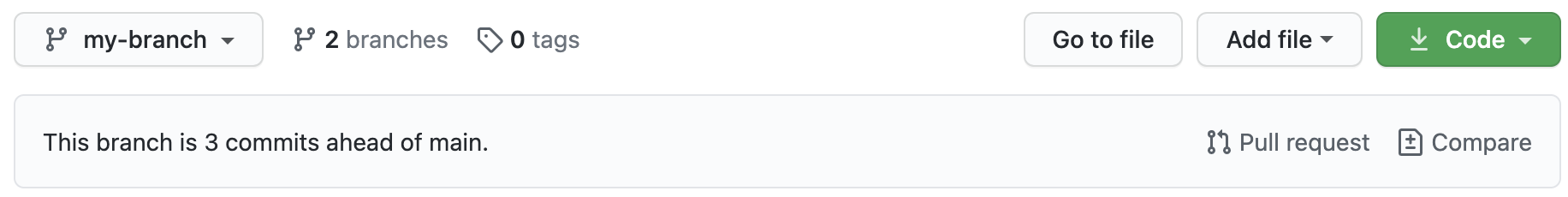
Click Pull request (on the right-hand side of the greyed-out box)
In the base: [branch-name] dropdown menu select the branch into which you'd like to merge your changes
In the compare: [branch-name] dropdown menu choose the branch containing your changes

Type in a title and comment for the pull request
Click the Create Pull Request button