Kotlin extensions provides us with ability to extend class with new functionalities.
To use Kotlin extensions, we simply put the prefix before function name. Prefix should be the type that is being extended, also known as receiver type.
Example:
fun View.hide() {
this.visibility = View.GONE
}
From the code snippet above, we can easily extend View objects with visibility functionality. This way we can easily change view visibility property using this one-liner function instead of writing boilerplate code.
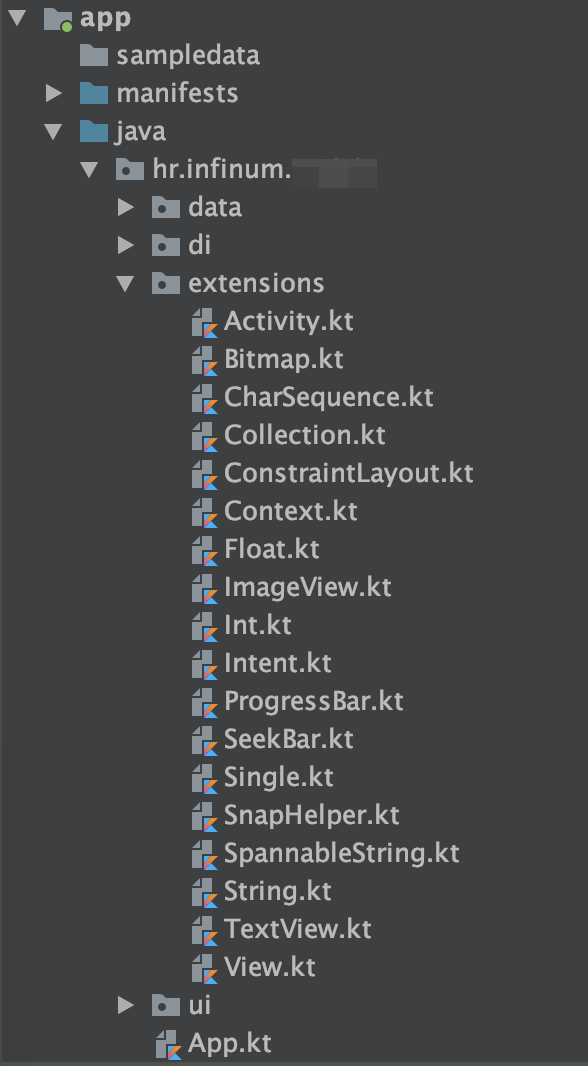
Where to use:
Kotlin extensions is a very powerful ability of Kotlin language and it can be used in various scenarios. While this is certainly a nice feature, it generates some clutter in our application packages and overall structure.
Good practice would be to include extension package on the same level as ui components. This way extensions are visible and are not "hidden" inside deeper levels of packages and folders.